SEM & DLS: Complementary Techniques for Particle Analysis
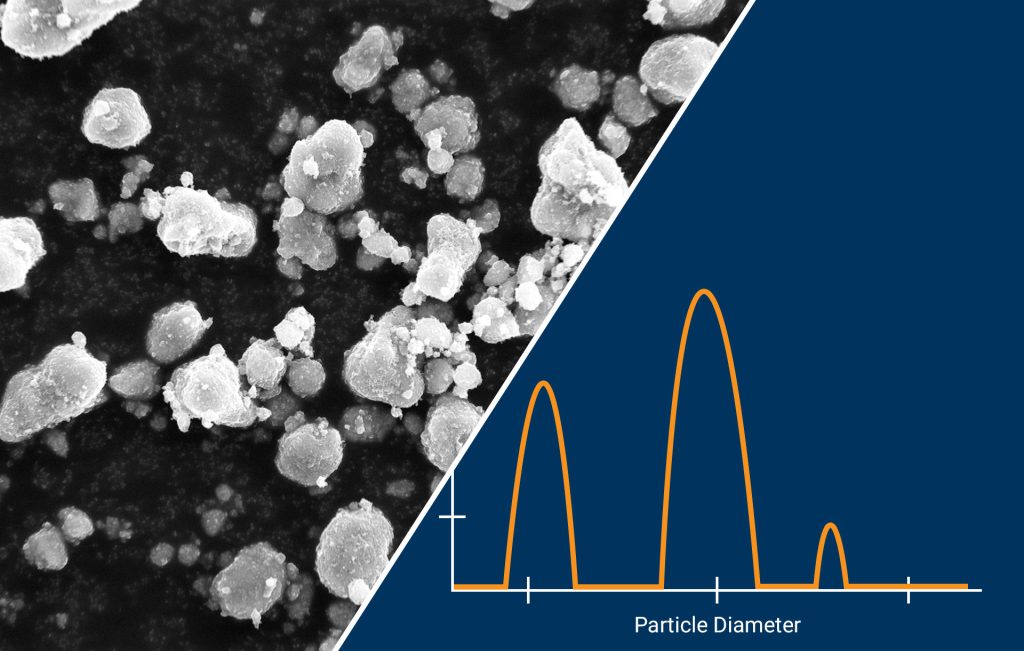
Analyzing particles is essential in a wide range of scientific and industrial fields. Particle characteristics such as size, shape and surface properties can affect the mechanical, optical, thermal and magnetic properties of the material and significantly influence the behavior and functionality of materials. The particle properties can also affect their performance in a range of […]
Electrospinning Nanoparticles for Biomedical Devices

Nanoparticles have revolutionized the field of biomedicine, playing a pivotal role in enhancing diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. When administered as free particles, nanoparticles face significant challenges, including rapid clearance from the bloodstream by the immune system and non-specific distribution throughout the body. These factors result in reduced effectiveness and potential toxicity. To overcome these challenges, […]
Electrospinning Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems
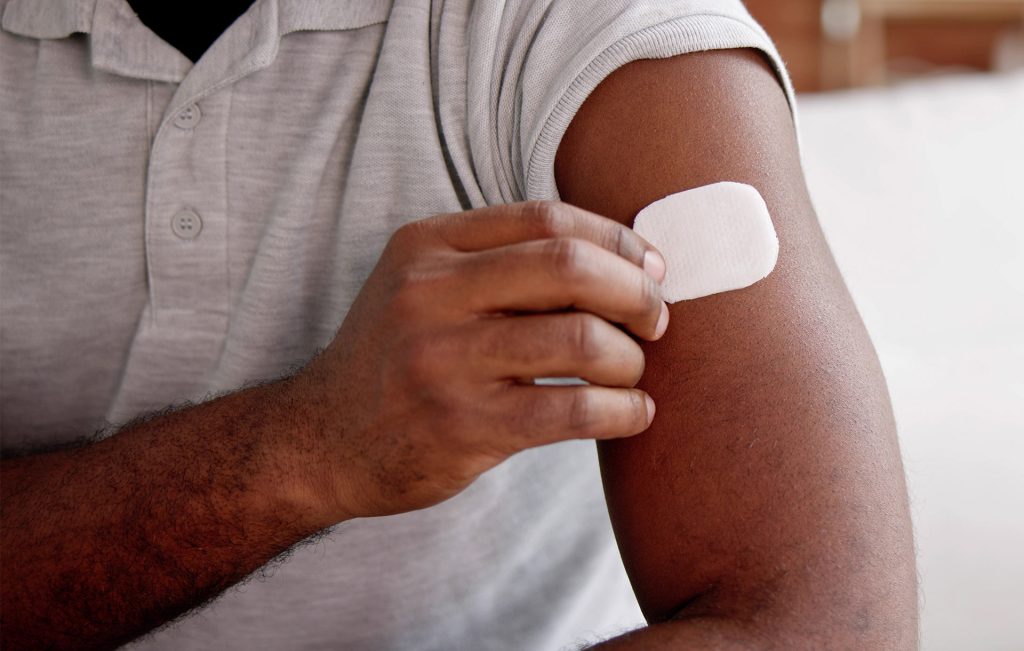
Transdermal drug delivery systems (TDDSs) use active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) to deliver therapeutic healing. However, many of these APIs are photosensitive and degrade when exposed to UV light sources. One of the most common ways TDDSs combat photodegradation is to use a blend of synthetic adhesives with APIs to deliver drugs while remaining adhered to a targeted site.
Electrospun Chitosan for Wound Healing Applications
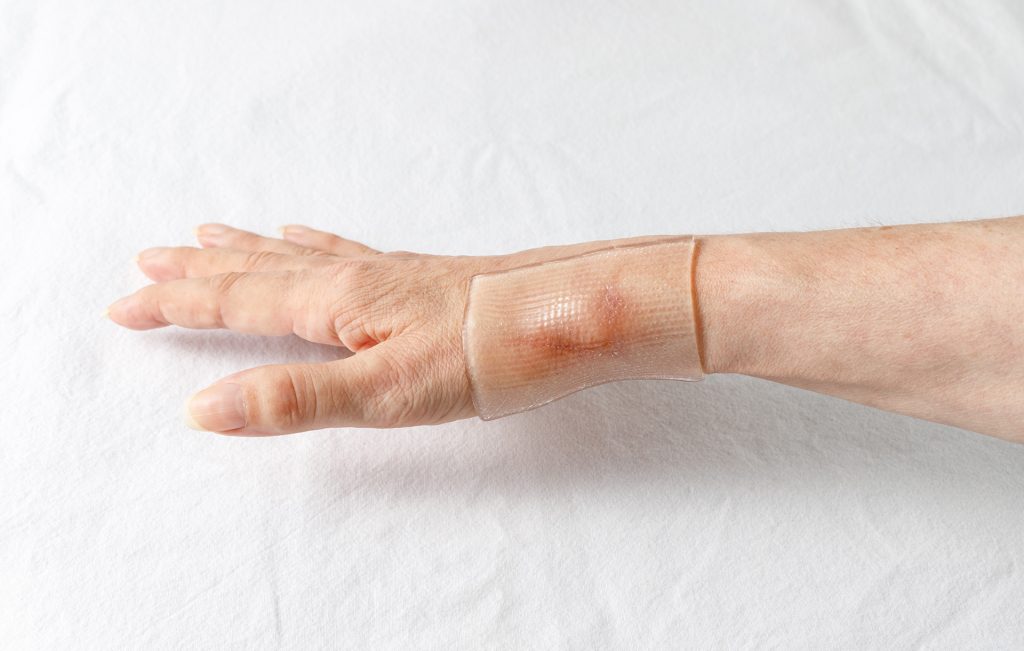
Skin injuries, infections, or diseases are a frequent occurrence within the general population. Oftentimes wound dressings or skin grafts are placed or implanted over the area of injury to assist with healing. The primary role of wound dressings is to isolate the site of injury from the environment and deliver drugs to allow the natural healing process to heal the wound. However, wound dressings require frequent exchanges irritating the injury site or pose an inherent risk to infection. Also, they do not play an active role in the healing process. Skin grafts on the other hand play an active role in the healing process. But many skin grafts either are limited in availability or pose a significant risk to rejection or infection.
Leveraging Electrospinning for Vascular Stent Coating
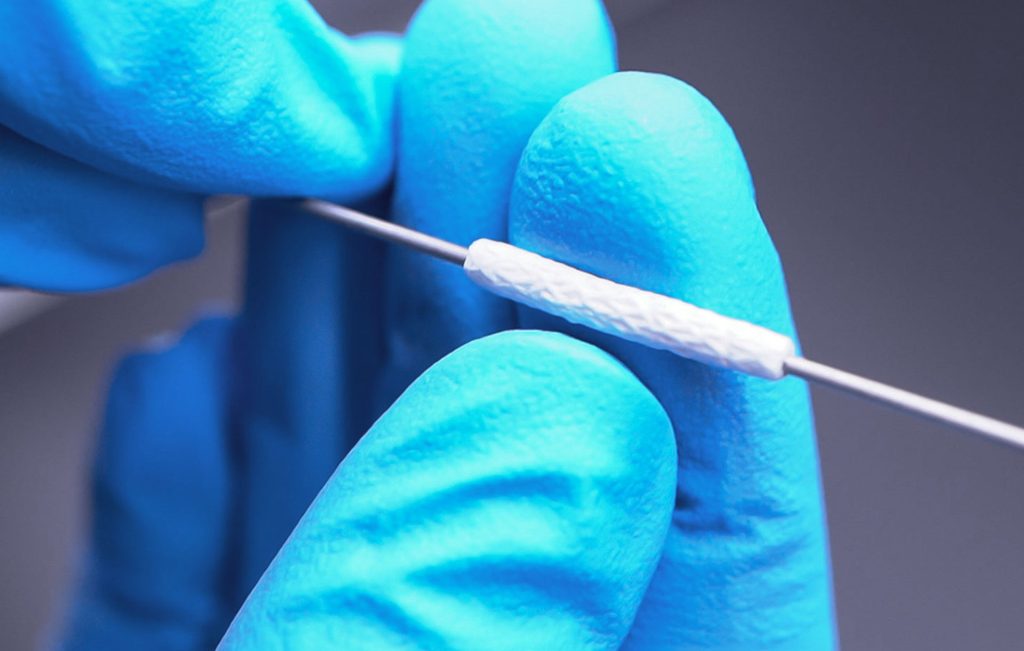
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is a powerful tool used to examine surfaces with high resolution. SEM works by scanning a sample’s surface with a focused electron beam to generate detailed, high-magnification images. However, imaging nonconductive materials, like polymers, textiles, and ceramics, can be challenging due to their inability to conduct electricity, which leads to charge buildup on the sample surface. This charge accumulation can distort the electron beam path, resulting in poor image resolution and quality. To address this fundamental issue, several methods are available to minimize charge buildup and optimize SEM imaging of non-conductive materials.
5 Approaches for Optimizing SEM Imaging of Nonconductive Samples
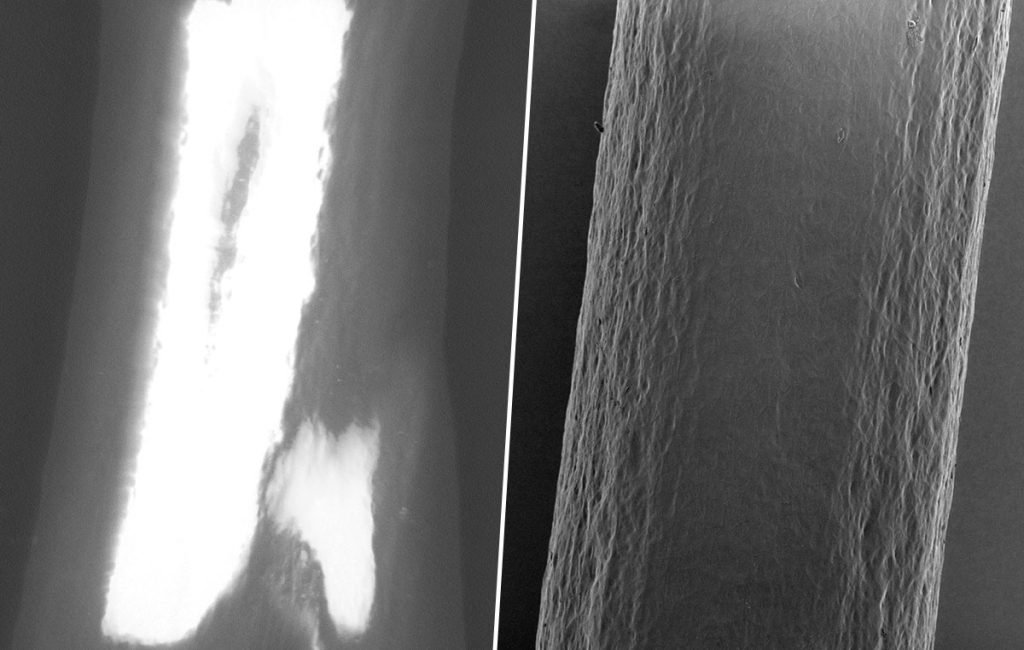
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) is a powerful tool used to examine surfaces with high resolution. SEM works by scanning a sample’s surface with a focused electron beam to generate detailed, high-magnification images. However, imaging nonconductive materials, like polymers, textiles, and ceramics, can be challenging due to their inability to conduct electricity, which leads to charge buildup on the sample surface. This charge accumulation can distort the electron beam path, resulting in poor image resolution and quality. To address this fundamental issue, several methods are available to minimize charge buildup and optimize SEM imaging of non-conductive materials.
An Overview of Electrospinning Vascular Grafts
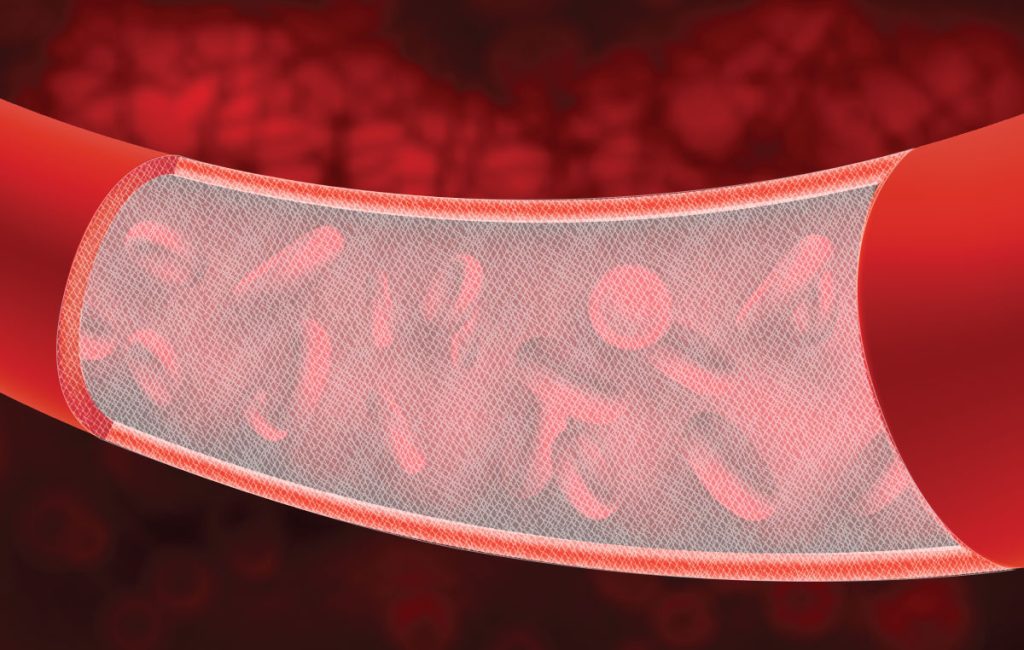
Cardiovascular diseases are a group of disorders of the heart and blood vessels and are the leading cause of death globally. Heart attacks and strokes account for 80% of these deaths and are primarily related to atherosclerosis, a condition resulting from the buildup of plaques in the arteries. Vascular grafts made of expanded Teflon (ePTFE) […]
Developing Electrospun Cosmetic Masks

Skincare products use either liquid-based or dry masks to deliver the active ingredients. Liquid-based delivery is limited since the active ingredients do not adhere well to the skin, preventing adequate absorption. Dry masks usually include chemical preservatives to maintain the shelf-life of active ingredients.
Scaling up the Fabrication of Electrospun Nanofibers
Electrospinning is a versatile technique that extrudes a polymer solution in a high-voltage field to fabricate fibers on the micro to nanoscales. Unlike other fiber production techniques, electrospinning can easily tune the fiber diameter (100 nanometers to a few micrometers), mechanical properties, and chemical functionality. While this technology shows promise within research settings, it is […]
Electrospun Carbon Nanofibers for High-Performance Applications
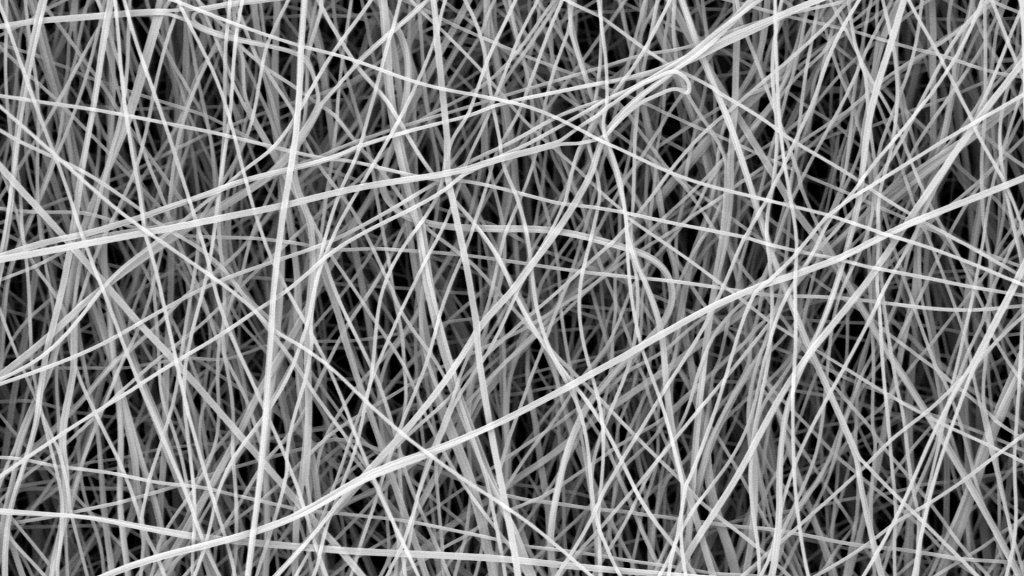

Carbon nanofibers hold great technological importance for a variety of high-performance applications. Due to their exceptional properties including being lightweight, having high electrical conductivity, thermal stability, and excellent mechanical properties, they are being used in a wide range of applications including energy, catalysis, and aerospace. Polyacrylonitrile (PAN) is a synthetic polymer resin that is used […]

